栈(stack)是一个先进后出(First In Last Out, FILO)的数据结构,在这里有对栈的数据结构进行过详细的讨论。
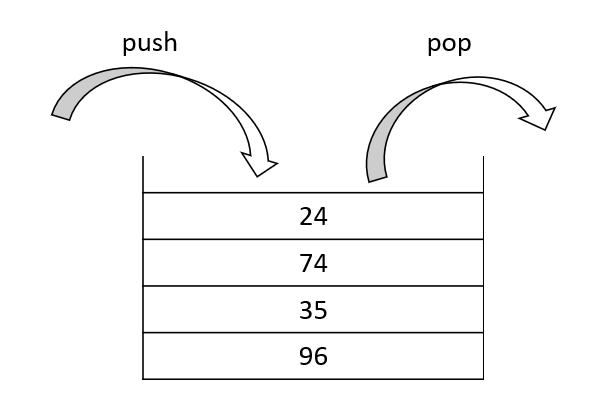
stack 提供如下几个操作:
push:将元素压入栈中pop:将栈顶元素弹出top:获得栈顶元素empty:判断栈是否为空size:获得栈中元素数量
STL 中的 stack
与利用栈顶元素及可以指向下一个元素的指针来实现栈不同,STL 中的栈利用已有的容器的实现。默认情况下 stack 利用 deque 实现。我们可以将 deque 有关前部的操作封闭,对后部的操作进行一层封装,如push可以利用deque.push_back()、top利用deque.back()。在 STL 中,除 deque 外,list、vector 均满足条件。
由于 stack 是利用其他容器的接口并进行修改实现的,所以一般将 stack 归类到容器适配器(Container Adapter),而不与 vector 这些归类至容器(Container)。
虽然说底层容器无论是 deque 还是 vector 均提供了迭代器,但是 stack 只有栈顶元素能被访问,所以 stack 不具有迭代器。
声明 & 实现
在模板类型中用Container来指定底层容器,之后就是对于容器的简单封装。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
template<class T,class Container=deque<T>>
class stack
{
public:
using container_type = Container;
using value_type =typename Container::value_type;
using size_type = typename Container::size_type;
using reference = typename Container::reference;
using const_reference = typename Container::const_reference;
protected:
Container c;
public:
explicit stack(const Container& cont):c(cont){}
stack(const stack& other):c(other.c){}
stack& operator=(const stack& other) {
c = other;
return *this;
}
reference top() { return c.back(); }
bool empty() const { return c.empty(); }
size_type size() const { return c.size(); }
void push(const value_type& value) { c.push_back(value); }
void push(value_type&& value) { c.push_back(std::move(value)); }
void pop() { c.pop_back(); }
};